I prepared a lesson plan with many applications and activities about technology based language learning. We all know that students love to be intertwined with technology. This program can teach them new things and help them use their imagination. Thanks to activities that cover the whole class, community awareness increases and becomes even more fun.If you want to use this lesson plan, you can download it from the link below.
Blog Feed
Activities for language learners
technology has a big place in our era for language learners.In technology enhanced education, providing students with various technology-related activities increases the students' desire, concentration and interest in the lesson.In order to help you, I put the jeopardy activity and activity template that I prepared as an example as a downloadable link.I hope it helps you in your lessons and helps you to produce interesting activities for your students.

Podcast Activities for Teachers
The purpose of this podcast it to share my podcast activity ideas that could be useful to teachers. You will listen to my activity suggestions and their beneficial sides for English learning and teaching. I hope it will beneficial for everyone who listens. The link is in below, check it out.
PODCASTS FOR LANGUAGE LEARNING
Since we are living in an internet-oriented world now, we should include the internet in our learning and teaching techniques. One of the unlimited resources available on the internet, podcast is a tool that will help us in this regard. Podcast, combination of the words “iPod” and “broadcast” and is the generic name for any continuing video and audio content you subscribe to. This article provides sufficient information about the usage of the podcast and reveals its advantages and disadvantages. Given in the Table 1 differences between digital immigrants and digital natives, we understand that they are both different from each other. “Today we can regard the students born as of 1990s into technology as digital natives and the earlier generations as digital immigrants. As the learner group mostly consists of digital natives their digital expectations should somehow be addressed. The advent of podcasting, within this context, is the subject matter of this paper and is covered in relation to its possible contributions to language learning and teaching processes.”
Pros
-Podcast can increase students’ interest and participation in class.
-Increases students’ listening skills, helps them improve their pronunciation.
-Can be used online but when you download you can use it anywhere offline.
-It is an endless source; it can be created by the student or teacher if there is no suitable content.
Cons
-It can be distractive sometimes.
-You have to pay to subscribe for some websites.
-Digital immigrant teacher may face some difficulties.
-You have to have technical knowledge to create a podcast.
Activities
Teachers can create podcasts in audio or video format and do quizzes to their students. Teachers can ask their students to prepare podcasts on the topic they want, and they can both check their pronunciation and get to know their students more closely.
By giving group podcast assignments, students can learn to work in groups, and they can also have fun.
I personally find podcasts useful in terms of learning technique. Because running the lesson from the book constantly or the teacher talking continuously causes loss of attention and boredom after a while. Watching videos or listening to audio during the lesson both prevents this from happening and it is more beneficial to listen to the language you learn from a native speaker.
Reference
– Prof. Dr. İsmail Yaman,THE POTENTIAL BENEFITS OF PODCASTS FOR LANGUAGE LEARNING, JOURNAL OF EDUCATIONAL AND INSTRUCTIONAL STUDIES IN THE WORLD
February 2016, Volume: 6 Issue: 1 Article: 07 ISSN: 2146-7463
Blogging for ELT
“A blog (short for weblog) is a frequently updated website that often resembles an online journal. It’s so easy to create and update a blog – it requires only basic access to the Internet, and a minimum of technical know-how.”
Three types of blogs are used in language teaching;
- The Tutor Blog (run by the teacher, content can be limited)
- The Class Blog (both teacher and the students can write, collaborative discussion space and more free)
- The Learner Blog (teacher sets it up, each student has an individual blog, requires more time and effort).
Using blogs provides reading and writing practice, increase the sense of community, encourage all students to participate, keeps students interested…etc
Pros
-Collective work space is provided not only at school but also at home.
-Commenting on each other allows students to see the right and wrong.
-Improves students’ reading, writing and grammar skills.
Cons
-Unwanted comments. (You can restrict comments if you want)
-It can be a problem for students who care about privacy. (You can change the privacy settings by talking to the teacher)
I think it might be suitable for students of all ages. While primary school students talk about their hobbies, phobias, and what they like to do, university students can write an article summary or response. it is useful for students as a collective environment. Provides an environment that you can share all kinds of assignments given by your teacher and your classmates also comment and share their ideas.
Reference
-https://www.teachingenglish.org.uk/article/blogging-elt
Technology and the four skills. Language, Learning and Technology
Most L2 instructors apply their curricula to develop four skills: speaking, listening, reading and writing. “This review article points out where computer-assisted language learning (CALL) can contribute to L2 language growth in terms of these four skills, especially if carefully situated within a task- based language teaching (TBLT) framework. This article examines the use of the CALL method in lessons and how students improve their language learning skills. Task-based language learning also means “learning by doing”, the thing that teachers want at the end of the class relating to speaking, listening, reading and writing.
Pros
- Students can access all kinds of resources over the internet.
- The activities that they do increase their interest in the lesson.
- Teachers use new techniques in education.
Cons
- Tasks that need to be done online may not be performed in environments without internet.
- students can deal with different things on their computers and complete the given tasks.
Activities
For speaking, students can be directed to programs where they can talk to foreign teachers or people.
For listening, teachers can create audio files that or find online and create activities for them thus, they make listening-supported activities for their students.
For reading, teachers can suggest reading articles appropriate for their students’ age and level or suggest sites for reading activity.
For writing, teachers can ask their students to research and write essay about it by giving them a specific topic.
In my opinion, the Internet has brought us comfort in every area. Using this comfort effectively in our lessons is something teachers and students must do.
Reference
-Blake, Robert. (2016). Technology and the four skills. Language, Learning and Technology. 20. 129-142.
TPACK
Technology became an important part of students’ lives, in the class it can help increase their understanding of complex things and collaboration among peers. because of such benefits, education system pushes teachers to use technology in their lessons. But most teachers have difficulties with this, especially with sufficient technological knowledge. Punya Mishra and Matthew J. Koehler’s 2006 TPACK framework, which focuses on technological knowledge (TK), pedagogical knowledge (PK), and content knowledge (CK), offers efficient approach to the many difficulties that the teachers face. “Thoughtful pedagogical uses of technology require the development of a complex, situated form of knowledge that we call Technological Pedagogical Content Knowledge (TPCK). In doing so, we posit the complex roles of, and interplay among, three main components of learning environments: content, pedagogy, and technology. “ The three types of knowledge are combined and recombined within the TPACK framework.
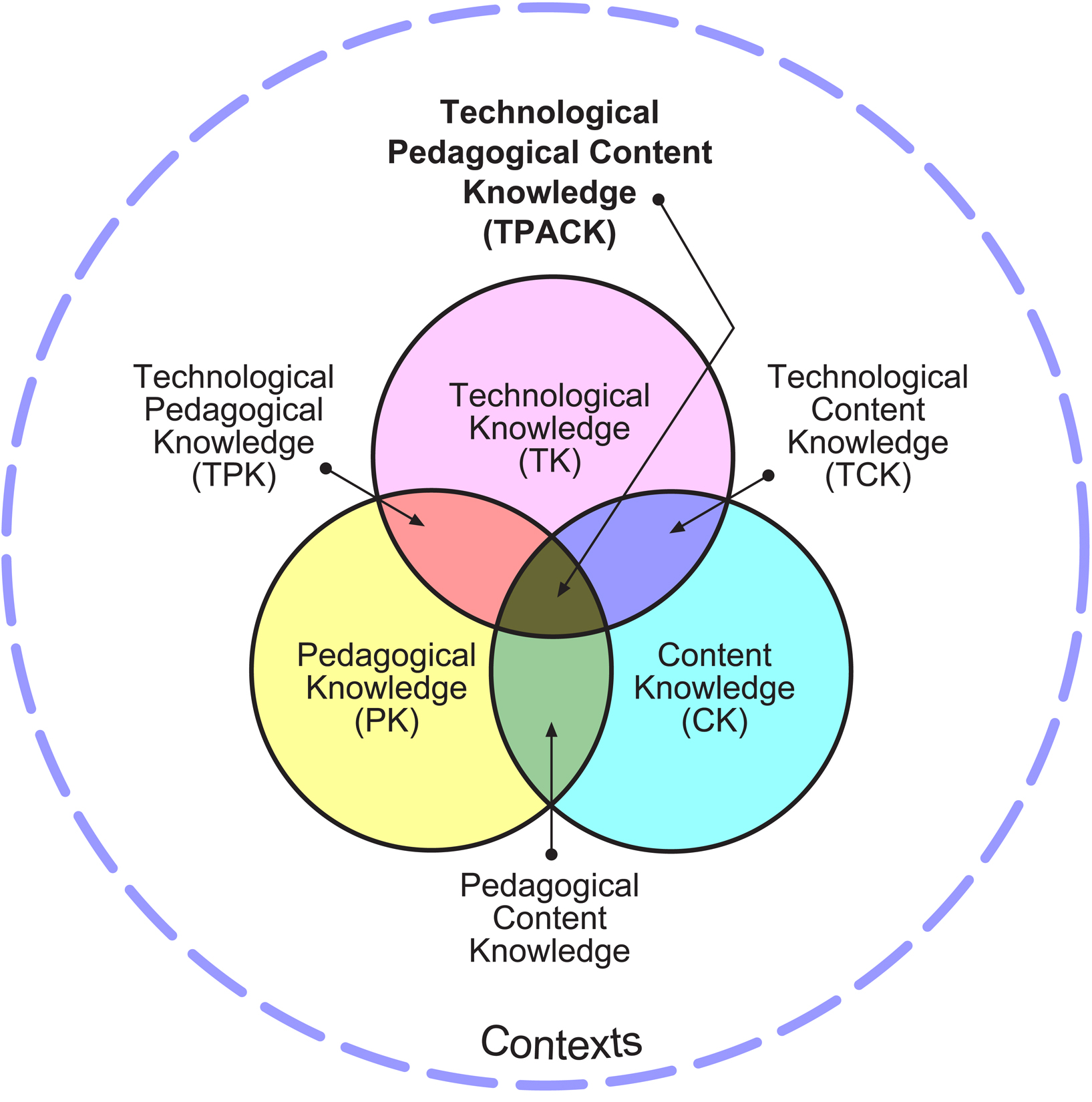
image ©2012 by tpack.org
Content Knowledge (CK) describes teachers knowledge of the subject matter
Pedagogical Knowledge (PK) describes teachers’ knowledge of the practices, processes, and methods regarding teaching and learning.
Technological Knowledge (TK) – This describes teachers’ knowledge of, and ability to use, various technologies, technological tools, and associated resources.
TPACK is useful inorder to make technology integration successful in the classroom.
References
- Mishra, P., & Koehler, M. J. (2006). Technological pedagogical content knowledge: A framework for integrating technology in teachers’ knowledge. Teachers College Record, 108 (6), 1017–1054
History Of Technology for L2 Learning
In the past years, many different types of tools have been used in foreign language learning and teaching. “The basic media used in language instruction—written texts, drawings, photos, audio, and video—have remained constant over time, although the technologies that delivered them have not. Technologies of the distant past seem quaint to us now, but issues and caveats voiced 100 years ago regarding technology and language learning still apply, even after decades of technological “advances” and changing perspectives on how best to approach language instruction.” During the first thirty years of the twentieth century, technology played an important role in some subjects, and over time, with the development of technology, it played a very important role in foreign language learning and teaching.
Periods and their names are listed below;
Early 20th century: Progressive eclecticism
Mid‐century: Repetition as the mother of learning
The 1960s to early 1980s: Interactivity and authenticity
The 1980s: Compelling new contexts
The 1990s: Toward new competencies
Early 21st century: The social turn
The technological tools used according to the periods are shown in the table below.

“Moreover, technology has advanced from its ancillary role in the curriculum to become a core source of content and a conduit for authentic language learning experiences. “
The combination of technology with ELT has changed dramatically over the past 25 years. Initially, it was limited to gap-filling activities and word activities, but then internet access, development of the web 2.0 and the arrival of the social web and mobile Technologies but currently, teachers and students are globally connected and can study globally.” Our understanding of the role of technologies in education has also evolved, and with it, the vocabulary we use to describe it. From the early beginnings of ‘computer-assisted language learning’ (CALL) through ‘technology-enhanced language learning’ to today’s emphasis on ‘information and communication technologies’ (ICT), we have lived through a period of huge change in this area of language education. “
Part 1: CALL In stage 1 Whilst Warschauer refers to ‘behaviouristic CALL in stage 2 Warschauer refers to ‘communicative CALL’, whilst Bax describes this incarnation as ‘open’. In stage 3 Warschauer refers to ‘Integrative’ CALL or ‘integrated’ CALL
Hardware: “Cheaper personal computers, colour monitors, and other useful hardware appeared. Computers acquired multimedia capabilities, adding richer colours and sound. Educational CD-ROMs, such as Encarta, were developed, and coursebooks started to include CD-ROMs with additional exercises and multimedia self-study material. “
Corpora “Corpus analysis particularly had a profound effect on course development and coursebooks as well as on dictionaries and other reference materials.”
Part 2: the great shift
Internet exchange: “Wider internet access in the late 1990s brought programs that increased the potential for culture-based global exchanges. These included early chat programs such as Internet Relay Chat and more entertaining interfaces including the now-defunct Microsoft Comic Chat “
WebQuests: “Allowing learners not only to work through a rich and varied research experience on the net, but also to transform this knowledge and form it into a range of ‘products’ as they worked.”
Websites and resources for teachers : “Alongside these early text-based communicative activities, innovators started to develop websites for English teachers, with ‘Dave’s ESL Café’ being one of the oldest and best known of the early ones. “
Online discussion groups and teacher training: “At the same time, teachers learnt how to subscribe to early discussion groups in their subject areas. Early such communities were TESL-L and NETEACH-L, both serving many purposes: not only discussing teaching itself, but also often leading to problem-solving discussions for people new to technology. “
Web 2.0 :” The major shift, arguably, was the technology transition from Web
1.0 (a static, expert-produced resource) to Web 2.0 (a more creative, consumer-driven space). The advent of Web 2.0 tools ensured that online users with no programming or design skills could now produce resources, and this led to more creative approaches from teachers using technology. “
IWBs : “In tandem with the rise of Web 2.0, we also saw the rise of more user-friendly (and more overtly familiar) tools such as the IWB “
Part 3: the future of technology in ELT
Mobile and blended learning :” The ubiquity of mobile or handheld devices, particularly mobile phones, has already seen them appearing in mainstream education teacher training. “
AR and game-based learning : “AR works by adding a virtual layer of information (in the form of text, images, or video) on to the real world. “
References
-From Past to Present: A Hundred Years of Technology for L2 Learning,SUE E. K. OTTO,The Handbook of Technology and Second Language Teaching and Learning, First Edition. Edited by Carol A. Chapelle and Shannon Sauro.
© 2017 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Published 2017 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
–ICT in ELT: how did we get here and where are we going?,Gavin Dudeney and Nicky Hockly,ELT Journal Volume 66/4 Special issue October 2012; doi:10.1093/elt/ccs050 © The Author 2012. Published by Oxford University Press; all rights reserved.